Payroll management is an essential task for any business, but it can also be one of the most time-consuming and error-prone processes. From calculating wages to deducting taxes, businesses face numerous challenges in handling payroll manually. The good news is that payroll automation in Canada is rapidly changing the way companies handle this task.
By automating payroll systems, businesses can save valuable time, reduce human errors, and improve the accuracy of their payroll processes. In this blog, we’ll break down how payroll automation works, its benefits, and the significant time and money savings businesses can achieve by embracing it.
What is Payroll Automation?
Before we look at the benefits, it’s important to understand what payroll automation is. Simply put, payroll automation refers to the use of software and tools to handle various payroll tasks automatically. Instead of manually calculating paychecks, deductions, and taxes, payroll automation tools can do this for you. The system takes into account hours worked, payslips, tax codes, and other variables to process payroll seamlessly and efficiently.
Payroll automation in Canada includes a variety of tools and systems designed to help businesses, regardless of size, streamline payroll processes. These systems handle everything from employee data management to tax calculations and reporting. This leads to reduced human error, fewer compliance issues, and faster payroll cycles.
Why is Payroll Automation Important for Businesses in Canada?

In Canada, businesses are subject to complex payroll laws, which include specific tax deductions, employee benefits, and compliance requirements. Payroll automation ensures businesses remain compliant with these regulations without the manual effort of staying updated on every change. It significantly reduces the chance of errors and helps mitigate the risk of penalties and fines due to inaccurate or delayed payroll processing.
Moreover, businesses in Canada face specific challenges when it comes to payroll due to regional tax laws, employment standards, and public benefits programs. By adopting payroll automation in Canada, businesses can avoid manual mistakes, ensure accurate reporting, and streamline their administrative workload.
The Benefits of Payroll Automation Canada
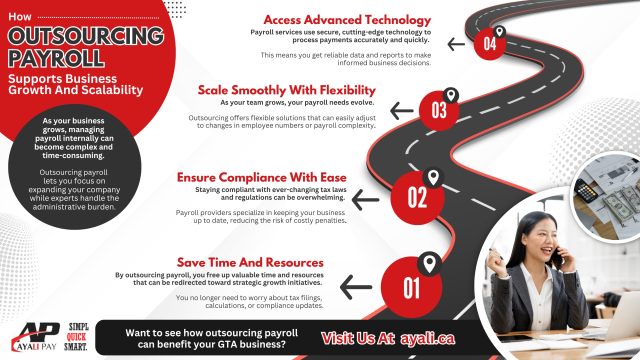
1. Time Savings

One of the most obvious advantages of payroll automation is the time it saves. With automated payroll systems, you no longer need to manually calculate each employee’s pay or deductions. The system takes care of all the calculations, leaving your HR or payroll team with more time to focus on other important tasks.
Let’s say, for example, that your business has 50 employees. Processing payroll manually could take hours, depending on the complexity of the pay structure and deductions. Payroll automation, however, could reduce this time significantly—often to just a few minutes.
This time-saving extends beyond just payroll processing. Payroll automation systems can also generate reports, update employee records, and send out payslips automatically. What once took days to complete can now be done in minutes.
2. Reduced Errors
Payroll errors can be costly. Small mistakes, such as incorrect tax calculations or misclassifying an employee, can lead to significant problems, including penalties from regulatory bodies like the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA).
By using payroll automation, these types of errors are greatly reduced. Payroll automation software uses pre-set rules, ensuring that tax deductions, benefit calculations, and other variables are consistent and accurate across all payroll runs. The software also updates automatically in line with changes to tax laws, eliminating the need for payroll managers to manually stay updated on every change.
3. Better Compliance
Payroll compliance is critical for any Canadian business. Employers must adhere to various federal, provincial, and municipal regulations, including tax reporting, employee benefits, and filing deadlines. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and penalties, as well as reputational damage.
Payroll automation in Canada helps businesses stay compliant by ensuring that taxes are calculated according to the latest government rules. Automated systems can also generate required reports and filings (such as T4 slips) and submit them directly to the CRA, ensuring your business meets all regulatory deadlines. Furthermore, these systems store records in an organized manner, making it easier to retrieve information in case of an audit or CRA payroll examination.
4. Cost Savings

Payroll automation doesn’t just save time; it also saves money. Manual payroll processing requires a significant amount of labour, which comes with a cost. If you’re handling payroll in-house, you may need to employ a dedicated payroll team, pay overtime, or hire an external consultant to ensure compliance.
A report commissioned by the Canadian Payroll Association found that Canadian employers spend $12.5 billion each year on payroll compliance. By automating payroll, you reduce the need for manual intervention, cutting down on staffing costs and overhead. For small businesses, this can be especially beneficial, as you no longer need to allocate a significant portion of your budget to payroll administration.
Additionally, automated systems typically reduce the risk of overpayments or underpayments, which can occur during manual payroll processing. By eliminating these costly errors, businesses can improve their bottom line.
5. Scalability
As your business grows, so does the complexity of your payroll. Managing a larger workforce requires handling more pay categories, benefit plans, and tax calculations, which can become overwhelming without the right tools. Payroll automation in Canada allows businesses to scale their payroll systems efficiently.
For example, if your company hires more employees, the automation system can quickly adapt to the changes, handling complex payroll scenarios with ease. The system can also generate reports and calculate payments for employees working in multiple provinces, all while adhering to the different tax laws in each region.
6. Improved Data Security
Payroll data is sensitive. It contains information about employee salaries, deductions, and personal details. Handling this information manually or using outdated systems can expose businesses to data breaches and compliance violations.
Payroll automation tools use the latest security measures, such as data encryption and secure cloud storage, to keep sensitive payroll data safe. These systems are also designed to restrict access to authorized personnel, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to private information.
7. Improved Employee Satisfaction
Automated payroll systems also benefit employees. By eliminating the risk of errors in paychecks, employees can be confident that they’re being paid accurately and on time. Payroll automation systems can also provide employees with easy access to their pay stubs and tax documents, making it simpler for them to manage their finances.
Furthermore, employees appreciate the transparency and reliability that comes with automated payroll systems. When employees don’t have to worry about payroll mistakes or delays, it creates a more positive work environment and improves overall satisfaction.
8. Access to Advanced Reporting Tools
Another significant advantage of payroll automation is the access it provides to advanced reporting tools. Payroll systems can generate detailed reports that provide valuable insights into your payroll expenses, tax liabilities, and employee compensation. These reports can help you make more informed business decisions and streamline your financial planning.
For example, you can track trends in overtime costs, analyze employee benefits usage, or monitor overall payroll spending to identify areas where you can reduce costs. These insights can be invaluable for businesses looking to optimize their financial management.
How Payroll Automation Tools Work in Canada
There are a variety of payroll automation tools available to businesses in Canada. Some of the most popular options include:
- Ceridian Dayforce:This tool is known for its reliable HR and payroll management capabilities. It offers features like real-time payroll calculations, employee self-service portals, and compliance with Canadian tax regulations.
- QuickBooks Payroll:This tool is widely used by small businesses across Canada. It simplifies payroll processing, including tax calculations, direct deposits, and automatic filing with the CRA.
- ADP Canada Payroll Services:ADP offers a comprehensive payroll solution that includes tax filing, payroll processing, and HR services. They also offer additional services like time tracking and compliance consulting.
These tools integrate with your existing HR software, automating the entire payroll process. Many of these tools also offer support during CRA audits, helping you stay compliant with Canadian tax laws and minimize the risk of penalties.
Return on Investment (ROI) of Payroll Automation in Canada

Investing in payroll automation can provide a significant return on investment (ROI) for businesses. By saving time, reducing errors, and improving compliance, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and operate more efficiently.
Consider a small business in Toronto with 25 employees. If it currently takes 10 hours to process payroll manually, that’s 520 hours annually spent on payroll tasks alone. By implementing an automated payroll system, that time could be reduced to just 2 hours per payroll run, saving the business 400 hours annually.
Assuming an average payroll manager earns $25 per hour, this translates to a savings of $10,000 per year. Additionally, the reduction in payroll errors and the associated penalties could save the business thousands of dollars in fines and overpayments.
Reliable Payroll Support for Canadian Businesses with Ayali Pay
Ayali Pay offers the best in payroll automation in Canada, making your payroll management not only easier but also more cost-effective. Ayali Pay stands out as a trusted payroll service provider in Canada, offering fully managed payroll services in the GTA that are tailored to the needs of both growing businesses and household employers. From accurate processing to full compliance, Ayali Pay also helps reduce the risk of issues related to a CRA payroll audit in Toronto by managing all government correspondence on your behalf.
Contact Ayali Pay today for hassle-free payroll services in Toronto.